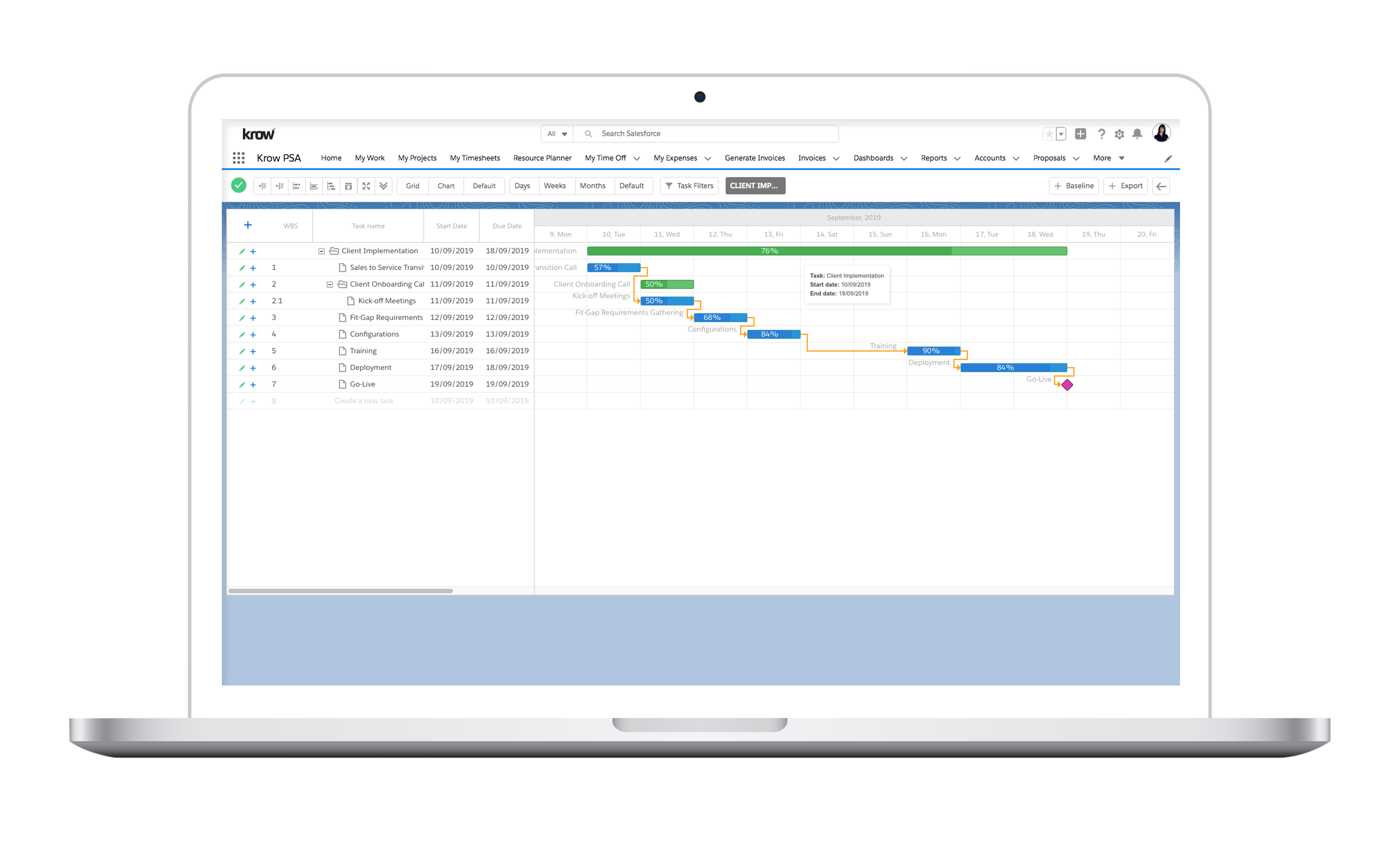
From Good to Great: How Competencies Can Elevate Your Project Management Skills
In this post, we’ll explore how competencies can elevate your project management skills from good to great and provide practical strategies for developing and measuring your competencies.
What are project management competencies?
Project management competencies refer to the knowledge, skills, and behaviors that enable a project manager to effectively plan, execute, and deliver projects. These competencies fall into three broad categories:
Technical competencies for Project Management
These are the technical skills and knowledge that project managers need to manage projects effectively, such as planning and scheduling, risk management, and budgeting.
- Project Planning: Project planning is a core technical competency for project managers. This includes developing project schedules, identifying and allocating resources, and developing project budgets.
- Risk management: Effective risk management is critical for project success. Project managers must be able to identify potential risks and develop strategies for managing and mitigating those risks.
- Budget management: Project managers must be able to manage project budgets effectively. This includes monitoring costs, tracking expenses, and adjusting as needed to ensure the project stays within budget.
- Quality management: Quality management is an essential technical competency for project managers. This includes developing quality standards, monitoring project quality, and ensuring project deliverables meet quality standards.
- Change management: Change is a constant in any project, and project managers must be able to manage change effectively. This includes developing change management plans, communicating changes to project stakeholders, and managing the impact of change on project scope, schedule, and budget.
- Technical skills: Project managers must have technical expertise in the areas that they are managing. This includes understanding the technical aspects of the project, the tools and technologies used, and the industry standards and best practices.
- Vendor management: Many projects involve working with external vendors or contractors, and project managers must be able to manage these relationships effectively. This includes developing vendor contracts, monitoring vendor performance, and ensuring that vendors meet project requirements.
Technical skills are a critical aspect of project management, and they can vary depending on the industry that the project manager will work in. For example, in software implementation, a project manager must have specific technical skills in order to effectively manage the project.
They must be able to understand the project requirements and translate them into specific tasks for the development team. They must also be able to work closely with the customer to ensure that their needs are met and that the project is delivered on time and within budget.
Other technical skills that are specific to software implementation may include knowledge of programming languages, software development tools, and testing methodologies.
By developing these specific technical skills, project managers in the software implementation industry can effectively manage projects and deliver high-quality software solutions to their clients.
Here are some examples of technical skills that may be specific to project managers in the software implementation industry:
- Proficiency in programming languages such as Java, Python, or JavaScript.
- Knowledge of software development tools such as Git, JIRA, or Agile software development methodologies.
- Familiarity with database management systems such as MySQL, Oracle, or SQL Server.
- Understanding of software testing methodologies such as unit testing, integration testing, or acceptance testing.
- Knowledge of cloud-based technologies and infrastructure such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure.
- Proficiency in project management software tools such as Microsoft Project or Asana.
- Understanding of software deployment and release management processes.
- Familiarity with software architecture and design principles.
By possessing these specific technical skills, project managers in the software implementation industry can effectively manage projects, work closely with development teams, and ensure that software solutions are delivered on time and within budget.
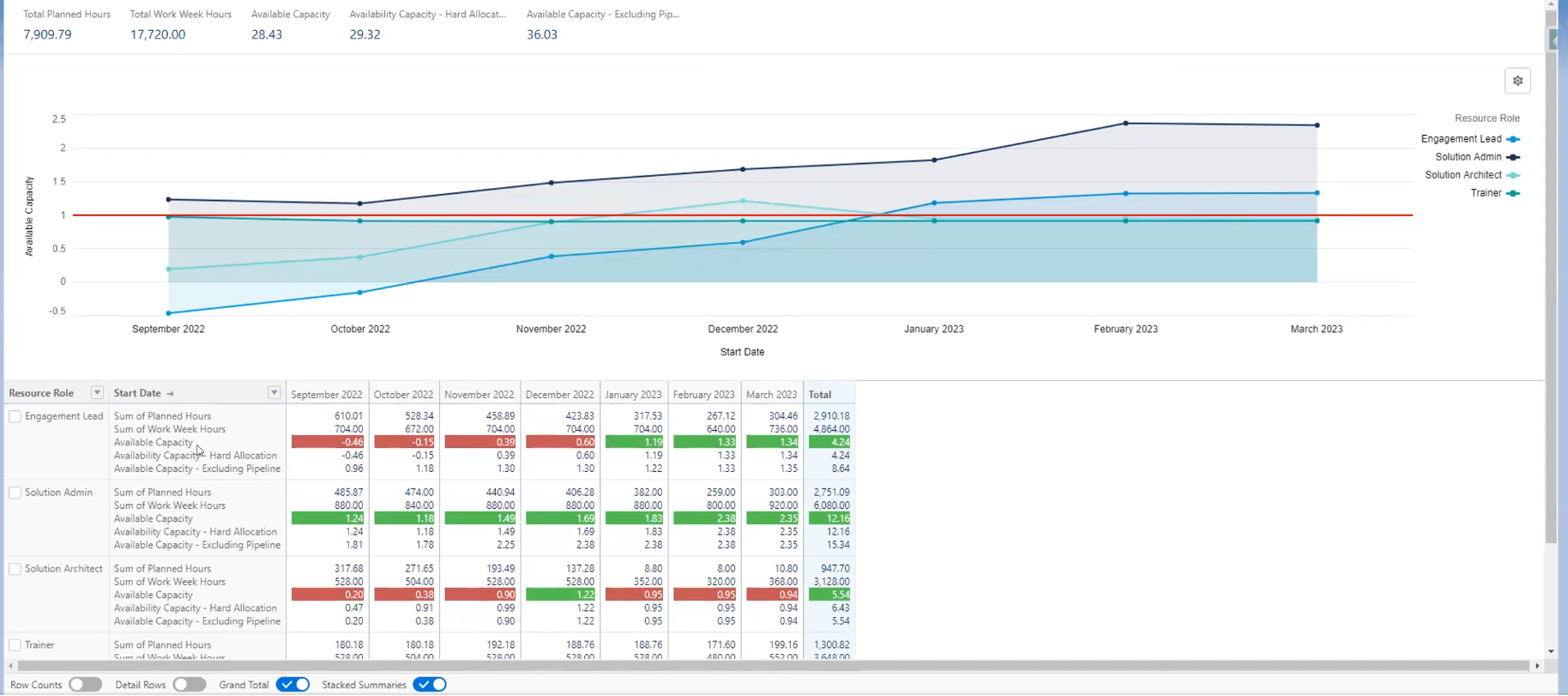
Behavioral competencies for Project Management
These are the interpersonal skills that project managers need to lead and motivate their teams, such as communication, conflict resolution, and leadership.
- Leadership: Effective project managers must be strong leaders, capable of motivating and inspiring team members, setting goals and objectives, and providing clear direction and guidance.
- Communication: Clear and effective communication is critical for project success. Project managers must be able to communicate project goals, objectives, and requirements to team members and stakeholders, and be able to provide feedback and guidance to team members as needed.
- Problem-solving: Project managers must be able to identify problems and develop effective solutions. This includes analyzing problems, developing options for resolving them, and implementing the best solution.
- Adaptability: Project managers must be able to adapt to changing circumstances and handle unexpected challenges. This includes being able to adjust project plans, timelines, and budgets as needed to respond to changing project requirements.
- Collaboration: Successful project managers must be able to collaborate effectively with team members, stakeholders, and external partners. This includes building relationships, working well in a team environment, and resolving conflicts effectively.
- Time management: Effective time management is essential for project success. Project managers must be able to prioritize tasks, manage their time effectively, and ensure that project milestones are met on time.
- Strategic thinking: Project managers must be able to think strategically, looking beyond the immediate project and identifying opportunities for long-term success. This includes considering project risks and opportunities, developing contingency plans, and making strategic decisions that support project success.
- Contextual competencies: these are the knowledge and skills that project managers need to navigate the organizational and environmental factors that impact their projects, such as stakeholder management, strategic thinking, and change management.
By developing these competencies, project managers can enhance their ability to lead successful projects, meet stakeholder expectations, and achieve business goals.

The key competencies for successful project management
There are several essential competencies that project managers must possess to be successful. These competencies are critical for managing the various aspects of a project and ensuring that it is completed on time, within budget, and to the desired quality standards. The key competencies for successful project management include:
Leadership and vision
Project managers need to provide clear leadership and vision for their teams. This involves setting clear project goals, defining project scope, and communicating project expectations. A good project manager should also be able to inspire and motivate their team to achieve these goals, and provide guidance and support as needed.
Here are some ways to be a good leader as a project manager:
- Set clear goals and expectations: Clearly communicate project goals and expectations to your team, and ensure that everyone is aligned on the project’s objectives.
- Delegate effectively: Delegate tasks to team members based on their skills and experience, and provide guidance and support as needed.
- Communicate effectively: Communicate project updates, risks, and challenges to team members and stakeholders, and provide timely feedback on performance.
- Be proactive: Anticipate potential issues and challenges, and develop contingency plans to address them before they become problems.
- Lead by example: Model the behavior and work ethic that you expect from your team, and be willing to roll up your sleeves and do the work alongside them.
- Provide support and guidance: Provide team members with the resources, tools, and training they need to be successful, and be available to answer questions and provide guidance as needed.
- Foster a positive team culture: Encourage open communication, collaboration, and innovation, and recognize and celebrate team achievements and successes.
- Be adaptable: Be flexible and adaptable in response to changing project requirements, and be willing to make adjustments to the project plan as needed.
- Encourage feedback: Encourage feedback from team members and stakeholders, and use this feedback to make improvements to the project and team performance.
By following these strategies, project managers can be effective leaders who inspire and motivate their team members, communicate effectively with stakeholders, and successfully deliver projects on time and within budget.
Communication
Effective communication is essential for successful project management. Project managers must be able to communicate project status, issues, and risks to stakeholders in a clear and concise manner. They also need to communicate expectations and goals to their team, and ensure that team members are communicating effectively with each other.
Effective communication is critical for project success, and as a project manager, it’s your responsibility to ensure that communication is clear, timely, and effective. Here are some strategies for great communication as a project manager:
- Set expectations: Establish clear expectations for communication with team members and stakeholders, and ensure that everyone understands the importance of timely and effective communication.
- Use the right communication channels: Use the appropriate communication channels for each situation, whether it be email, phone, video conference, or in-person meetings.
- Develop a communication plan: Develop a communication plan that outlines the communication needs of the project, including who needs to be informed, what information needs to be shared, and how often communication should occur.
- Listen actively: Listen actively to team members and stakeholders, and ensure that their concerns and questions are heard and addressed.
- Be clear and concise: Use clear, concise language in all communication, and avoid jargon or technical terms that may be unclear to some team members or stakeholders.
- Provide regular updates: Provide regular updates on project progress, risks, and challenges to team members and stakeholders, and ensure that all communication is timely and accurate.
- Be transparent: Be transparent about project risks and challenges, and be willing to provide honest and transparent communication about project status, even if the news is not always positive.
- Use visuals: Use visuals such as charts, diagrams, and tables to communicate complex information in a clear and concise manner.
- Ask for feedback: Ask for feedback from team members and stakeholders on the effectiveness of communication, and use this feedback to make improvements to communication processes.
By following these strategies, project managers can ensure that communication is clear, timely, and effective, and can help to ensure project success.
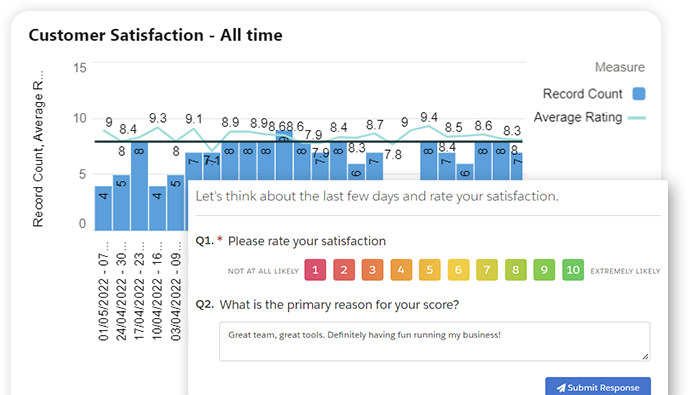
Time management
Time management is a critical competency for project managers, as they are responsible for ensuring that projects are completed on time. This involves developing realistic project schedules, monitoring progress against these schedules, and making adjustments as needed.
Time management is essential for project success, and as a project manager, it’s your responsibility to ensure that the project stays on track and is delivered on time. Here are some strategies for optimizing time management in a project:
- Develop a project schedule: Develop a detailed project schedule that outlines all project tasks and timelines, and ensure that team members are aware of their deadlines and responsibilities.
- Prioritize tasks: Prioritize project tasks based on their importance and urgency, and ensure that team members are aware of the critical path and dependencies.
- Use time tracking tools: Use time tracking tools to monitor project progress and ensure that team members are staying on track.
- Set realistic timelines: Set realistic project timelines based on the scope of the project and the resources available, and avoid overpromising and under delivering.
- Break down tasks: Break down project tasks into smaller, more manageable tasks, and assign them to team members based on their skills and experience.
- Eliminate distractions: Eliminate distractions such as unnecessary meetings or interruptions, and encourage team members to focus on their work.
- Automate processes: Automate processes such as reporting or data entry, to save time and reduce the risk of errors.
- Regularly review and adjust the schedule: Regularly review the project schedule and adjust timelines and tasks as needed, to ensure that the project stays on track.
- Use project management software: Use project management software to help manage the project schedule, monitor progress, and communicate with team members and stakeholders.
By following these strategies, project managers can optimize time management in their projects, and ensure that the project is delivered on time and within budget.
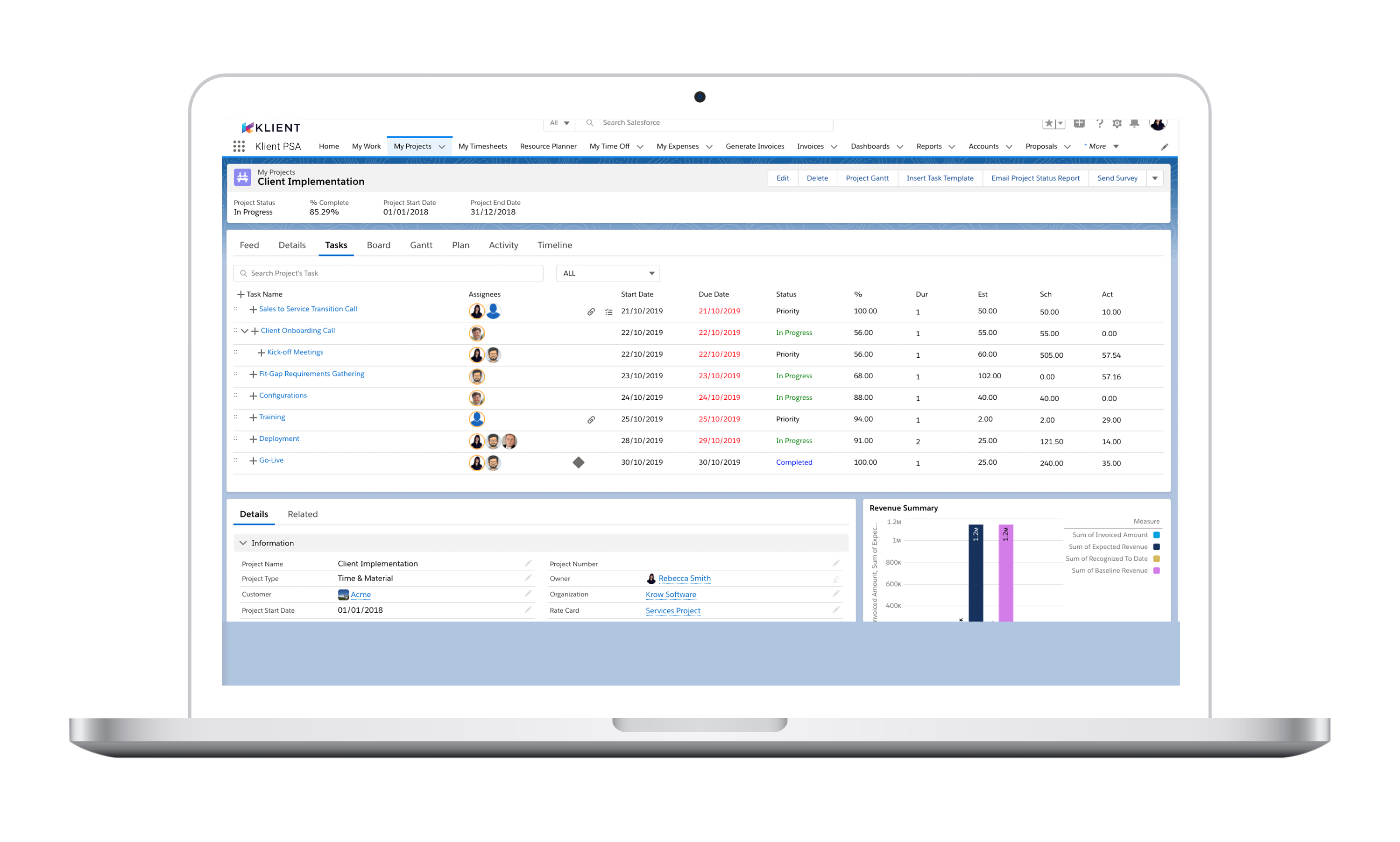
Budgeting and financial management
Project managers must also have a strong understanding of budgeting and financial management. This involves creating project budgets, monitoring expenses, and ensuring that projects are delivered within budget.
Ensuring that a project stays within budget is a critical aspect of project management. Here are some strategies for managing project budgets and ensuring that they stay on target:
- Develop a detailed project budget: Develop a detailed project budget that includes all project expenses, including labor, materials, equipment, and any other costs associated with the project.
- Track expenses: Track project expenses carefully, and ensure that all expenses are properly recorded and accounted for.
- Manage costs: Manage project costs carefully, and look for opportunities to reduce costs or eliminate unnecessary expenses.
- Monitor the budget: Monitor the project budget carefully, and compare actual expenses to the budget on a regular basis.
- Adjust the budget as needed: Adjust the project budget as needed to account for changes in project scope or unexpected expenses.
- Use forecasting tools: Use forecasting tools to project project expenses and identify potential cost overruns before they occur.
- Involve the project team: Involve the project team in the budget management process, and encourage them to identify opportunities to reduce costs and manage expenses.
- Manage project risks: Manage project risks carefully, and develop contingency plans to address potential cost overruns or unexpected expenses.
- Communicate regularly with stakeholders: Communicate regularly with stakeholders about the project budget, and provide regular updates on project expenses and any changes to the budget.
By following these strategies, project managers can effectively manage project budgets and ensure that they stay on target, while also delivering a high-quality project that meets the needs of stakeholders.
Risk management
Risk management is an important competency for project managers, as they are responsible for identifying and managing project risks. This involves developing risk management plans, monitoring risks, and taking corrective action as needed.
Creating and using project templates can help project managers to manage similar projects more effectively and efficiently, and can help to identify potential risks and challenges before they become major issues. Here are some strategies for creating and using project templates:
- Identify common project elements: Identify the common elements of projects that your team manages regularly, including project scope, requirements, timelines, and deliverables.
- Develop a project template: Develop a project template that includes all common project elements, and use this template as a starting point for new projects.
- Customize the template as needed: Customize the project template for each new project, based on the specific requirements and scope of the project.
- Identify potential risks and challenges: Use the project template to identify potential risks and challenges that may arise during the project, and develop contingency plans to address these issues.
- Use the template to track progress: Use the project template to track project progress and ensure that the project is staying on track.
- Review and adjust the template regularly: Review the project template regularly and make adjustments as needed to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
- Encourage team feedback: Encourage team members to provide feedback on the project template and suggest improvements to make it more effective.
By following these strategies, project managers can use project templates to effectively manage similar projects, identify potential risks and challenges, and ensure that the project is delivered on time and within budget.
Problem solving and decision making
Project managers need to be able to effectively solve problems and make decisions that impact project outcomes. This involves analyzing information, identifying options, and selecting the best course of action.
Stakeholder management
Project managers must also be able to effectively manage project stakeholders. This involves identifying stakeholders, understanding their needs and expectations, and ensuring that they are engaged and informed throughout the project.
Team building and collaboration
Finally, project managers must be able to build and lead high-performing project teams. This involves creating a positive team culture, managing team dynamics, and promoting collaboration and teamwork.
By developing these key competencies, project managers can elevate their skills from good to great, and achieve greater success in their project management careers.
How to develop project management competencies
Developing project management competencies is an ongoing process that requires a combination of training, coaching, and on-the-job experience. Here are some strategies for developing your competencies:
Training and development programs
There are many training and development programs available for project managers, ranging from online courses to formal degree programs. These programs can help project managers develop their technical, behavioral, and contextual competencies, and provide opportunities to network with other project managers.
Here are some free online courses for project managers:
- Project Management Principles and Practices Specialization (Coursera) – This specialization, offered by the University of California, Irvine, includes five courses that cover project management principles and practices, including planning, scheduling, and risk management.
- Project Management for Beginners (Udemy) – This course covers the basics of project management, including project planning, budgeting, and risk management.
- Introduction to Project Management (Alison) – This course provides an introduction to project management principles and practices, including planning, scheduling, and budgeting.
- Fundamentals of Project Planning and Management (edX) – This course, offered by the University of Virginia, covers the fundamentals of project planning and management, including project scheduling, budgeting, and risk management.
- Project Management Essentials (LinkedIn Learning) – This course covers the essentials of project management, including project planning, scheduling, budgeting, and risk management.
- Successful Project Management (OpenLearn) – This course, offered by The Open University, covers the key principles of project management, including planning, budgeting, and risk management.
- Project Management Basics (Skillshare) – This course covers the basics of project management, including project planning, scheduling, and budgeting.
These free online courses can help project managers enhance their skills and competencies, and gain valuable knowledge and insights into project management principles and practices.
Mentoring and coaching
Mentoring and coaching can be valuable tools for developing project management competencies. A mentor can provide guidance and support as you navigate your career, while a coach can help you identify and address specific competency gaps.

Asking for mentoring and coaching as a project manager can be a great way to improve your skills and competencies. Here are some steps to follow when asking for mentoring and coaching:
- Identify your goals and objectives: Before you approach a potential mentor or coach, it’s important to identify your goals and objectives for the mentoring or coaching relationship. This can help you identify the specific areas where you need help, and make it easier to communicate your needs to the mentor or coach.
- Identify potential mentors or coaches: Next, identify potential mentors or coaches who have the skills and experience that align with your goals and objectives. You can reach out to people in your network, attend industry events or conferences, or use online resources to find potential mentors or coaches.
- Reach out to potential mentors or coaches: Once you’ve identified potential mentors or coaches, reach out to them and introduce yourself. Explain your goals and objectives for the mentoring or coaching relationship, and ask if they would be willing to provide guidance and support.
- Schedule a meeting or call: If the mentor or coach is willing to provide guidance and support, schedule a meeting or call to discuss your goals and objectives in more detail. This can help you establish a plan for the mentoring or coaching relationship and ensure that you’re both on the same page.
- Be clear about expectations: It’s important to be clear about your expectations for the mentoring or coaching relationship, including the frequency of meetings or calls, the topics that will be covered, and any specific goals or objectives that you want to achieve. This can help ensure that you get the most out of the mentoring or coaching relationship.
- Follow through on commitments: Finally, it’s important to follow through on your commitments as a mentee or coaching recipient. This can include preparing for meetings or calls, taking notes, and implementing the guidance and advice provided by the mentor or coach.
By following these steps, you can successfully ask for mentoring and coaching as a project manager and gain valuable guidance and support to help you improve your skills and competencies.
On-the-job learning and experience
One of the most effective ways to develop project management competencies is through on-the-job learning and experience. By working on a variety of projects and taking on new responsibilities, project managers can gain valuable experience and build their competencies.
Professional certifications and education
Professional certifications and education can also be valuable for developing project management competencies. There are several certifications available for project managers, such as the Project Management Professional (PMP) certification, which can demonstrate your competency level to employers and clients.
There are several certifications available for project managers, but some of the most popular and widely recognized certifications include:
- Project Management Professional (PMP) – offered by the Project Management Institute (PMI), this certification is widely recognized as the most prestigious and in-demand certification for project managers.
- Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) – also offered by the PMI, this entry-level certification is designed for those who are new to project management.
- PRINCE2 – offered by AXELOS, this certification is widely recognized in the UK and Europe, and is growing in popularity in other parts of the world.
- Agile Certified Practitioner (ACP) – also offered by the PMI, this certification is designed for project managers who work in Agile environments.
- Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) – offered by the Scrum Alliance, this certification is specifically focused on the Scrum methodology, which is commonly used in Agile project management.
- Certified Project Manager (CPM) – offered by the International Association of Project Managers (IAPM), this certification is focused on project management principles and practices, and is designed for project managers at all levels of experience.
- Certified Project Management Practitioner (CPMP) – offered by the Global Association for Quality Management (GAQM), this certification covers project management principles and practices, as well as leadership and strategic management.
These certifications can help project managers enhance their skills, knowledge, and competencies, and demonstrate their proficiency to employers and clients.
Measuring project management competencies
Measuring project management competencies is an important part of professional development. By assessing your competencies, you can identify areas for improvement and develop a plan for further development. Here are some ways to measure project management competencies:
Measuring your performance as a project manager is important to help you identify areas for improvement and continue to develop your skills and competencies. Here are some ways to measure your performance as a project manager:
- Use project performance metrics: As a project manager, you should be tracking project performance metrics such as project completion rate, schedule variance, cost variance, earned value, customer satisfaction, quality metrics, risk metrics, resource utilization, and time to market. By measuring these metrics, you can assess how well you are managing the project and identify areas for improvement.
- Seek feedback from stakeholders: You can seek feedback from project stakeholders, including team members, customers, and sponsors, to gain insight into how you are performing as a project manager. You can use feedback tools, interviews, focus groups, performance reviews, peer reviews, and self-assessment to gather feedback. This feedback can help you identify your strengths and areas for improvement, and adjust your project management approach accordingly.
- Evaluate your performance against project objectives: You should regularly evaluate your performance against the project objectives and goals to determine whether you are on track or need to make adjustments. This evaluation can be done using a project dashboard or scorecard that captures the progress of the project against key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Reflect on your own performance: Self-reflection is an important tool for measuring your performance as a project manager. You can ask yourself questions such as: What did I do well on this project? What could I have done differently? What did I learn from this project? By reflecting on your own performance, you can identify areas for improvement and develop a plan to address them.
- Use professional development tools: You can use professional development tools such as training, certification, and mentoring to help you improve your performance as a project manager. These tools can help you acquire new skills, knowledge, and competencies, and improve your overall performance as a project manager.
By using these approaches, you can measure your performance as a project manager and make the necessary adjustments to improve your skills and competencies.
Self-assessment tools and techniques
Self-assessment tools and techniques can be used to assess your competency level in various areas of project management. These tools may include competency assessments, skills inventories, or 360-degree feedback.
Here are some self-assessment tools for project managers:
- Competency assessments: Competency assessments are self-assessments that measure a project manager’s level of proficiency in various project management competencies, such as leadership, communication, time management, and risk management. These assessments can help project managers identify their strengths and areas for improvement and develop a plan to address any competency gaps.
- Skills inventories: Skills inventories are self-assessments that measure a project manager’s skills in various areas, such as project planning, budgeting, risk management, and communication. These assessments can help project managers identify their strengths and areas for improvement and develop a plan to enhance their skills.
- Self-reflection exercises: Self-reflection exercises are tools that project managers can use to reflect on their performance and behavior in various project management situations. These exercises can help project managers identify their strengths and areas for improvement and develop a plan to address any issues.
- Personality assessments: Personality assessments are self-assessments that measure a project manager’s personality traits, such as extraversion, openness, and conscientiousness. These assessments can help project managers better understand their personal strengths and limitations and develop a plan to work more effectively with others.
- Emotional intelligence assessments: Emotional intelligence assessments are self-assessments that measure a project manager’s emotional intelligence, such as self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills. These assessments can help project managers identify their emotional strengths and areas for improvement and develop a plan to improve their emotional intelligence.
These self-assessment tools can help project managers better understand their strengths and limitations and develop a plan to improve their performance and competencies as project managers.
360-degree feedback
360-degree feedback involves soliciting feedback from a variety of sources, including managers, peers, and direct reports. This feedback can help project managers gain a more comprehensive understanding of their competencies and identify areas for improvement.
Here are some ways that project managers can get 360-degree feedback:
- Online feedback tools: There are several online feedback tools available that allow project managers to collect feedback from their colleagues, team members, and other stakeholders. These tools typically use a survey format to gather feedback and provide the project manager with a report summarizing the results.
- Interviews: Project managers can conduct interviews with their colleagues, team members, and other stakeholders to gather feedback. These interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or via video conferencing, and can provide a more in-depth understanding of the feedback.
- Focus groups: Focus groups can be used to gather feedback from a group of stakeholders, such as team members, customers, or suppliers. This approach can be especially useful for identifying trends and common issues across the project.
- Performance reviews: Project managers can use performance reviews to gather feedback from their supervisors, colleagues, and team members. These reviews can be formal or informal, and should provide a clear understanding of the project manager’s strengths and areas for improvement.
- Peer review: Project managers can use a peer review process to gather feedback from other project managers within their organization. This approach can provide valuable insights and perspectives from others in similar roles.
- Self-assessment: Project managers can also gather feedback through a self-assessment process. By reflecting on their own performance and seeking feedback from others, project managers can gain a better understanding of their own strengths and areas for improvement.
These approaches can help project managers gather comprehensive 360-degree feedback, which can be used to identify areas for improvement, build on their strengths, and continue to develop their competencies as project managers.
Performance appraisals and evaluations
Performance appraisals and evaluations can also be used to assess project management competencies. By setting clear performance goals and metrics, project managers can track their progress and identify areas for improvement.
Performance appraisals and evaluations can be conducted using the OKR (Objectives and Key Results) method for project managers. Here’s how to use the OKR method for performance appraisals and evaluations:
- Set project objectives: The first step is to set project objectives that are aligned with the organization’s goals. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Each objective should also be tied to a specific outcome or result.
- Define key results: Once the project objectives are set, the next step is to define key results that will indicate progress toward achieving the objectives. These key results should be specific, measurable, and tied to the project objectives. Key results can be quantitative or qualitative, and they should be challenging yet achievable.
- Monitor progress: Throughout the project, project managers should regularly monitor progress toward achieving the objectives and key results. This can be done using project management software, a project dashboard, or other monitoring tools. Progress should be tracked against the key results and compared to the project objectives.
- Conduct performance appraisals and evaluations: At the end of the project, project managers should conduct performance appraisals and evaluations using the OKR method. This involves comparing the actual results achieved against the key results and project objectives. Any gaps between the actual results and the objectives should be identified, and a plan should be developed to address these gaps.
- Use feedback for continuous improvement: Feedback from the performance appraisals and evaluations should be used for continuous improvement. This can involve identifying areas for improvement, developing a plan to address these areas, and implementing changes to improve performance on future projects.
By using the OKR method for performance appraisals and evaluations, project managers can ensure that their performance is aligned with the organization’s goals, and that they are making progress toward achieving these goals.
It also provides a clear and objective way to evaluate performance and identify areas for improvement, which can lead to better performance on future projects.
Project performance metrics
Finally, project performance metrics can be used to measure the impact of project management competencies on project outcomes. By tracking project performance metrics, project managers can identify areas for improvement and adjust their competencies accordingly.
Here are some project performance metrics that project managers can use to measure the success of their projects:
- Project completion rate – measures the percentage of tasks or milestones completed on time and within budget.
- Schedule variance (SV) – measures the difference between the planned schedule and the actual schedule of the project.
- Cost variance (CV) – measures the difference between the planned budget and the actual budget of the project.
- Earned value (EV) – measures the actual value of work completed compared to the planned value of work to be completed.
- Return on investment (ROI) – measures the financial return on the project investment.
- Customer satisfaction – measures how satisfied the project stakeholders are with the project outcome and deliverables.
- Quality metrics – measures the quality of the project deliverables and outcomes.
- Risk metrics – measures the identification, assessment, and mitigation of project risks.
- Resource utilization – measures how effectively project resources, such as people, time, and money, are being used.
- Time to market – measures the time it takes to deliver a project and get it to the market.
These project performance metrics can be used to evaluate the project’s success, identify areas for improvement, and track the progress of the project.
By measuring project performance metrics, project managers can make informed decisions, adjust their project management strategies, and ensure the success of their projects.
Conclusion
Project management competencies are essential for successful project management.
By developing key competencies such as leadership, communication, time management, and risk management, project managers can elevate their skills from good to great, and achieve greater success in their careers.
Through training, mentoring, and on-the-job experience, project managers can continue to develop and strengthen their competencies, and by measuring their competencies, they can identify areas for improvement and develop a plan for further development.

You liked this Klient Tip? Share it with your team!
Discover more articles from Klient
Replace all your tools with Klient, Salesforce #1 PSA platform
Run your entire SaaS and consulting business on a single professional service automation platform native to Salesforce!